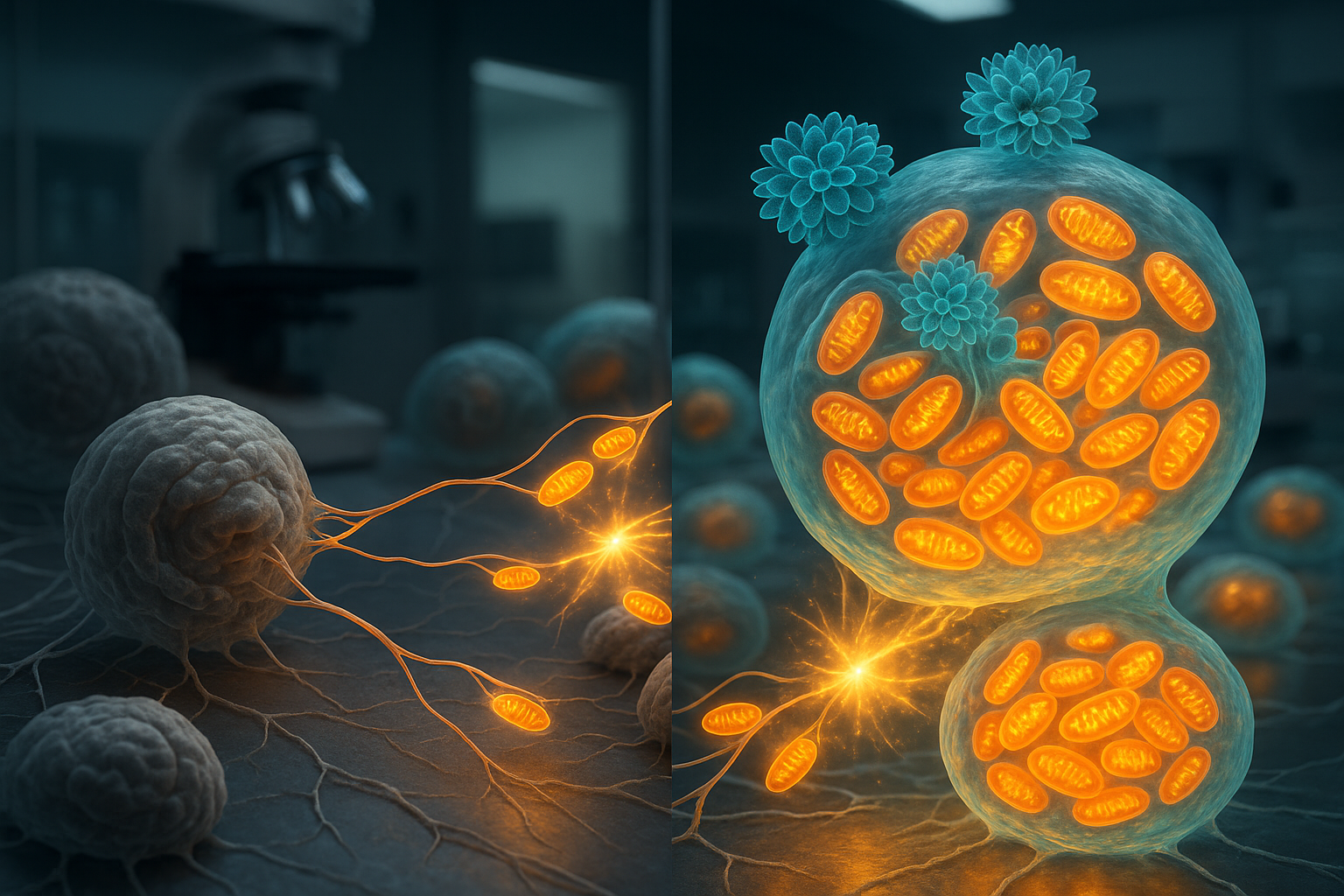
Biomedical engineers at Texas A&M University have used nanoflowers to make stem cells produce roughly twice the usual number of mitochondria. These enhanced stem cells then transfer the extra energy-producing organelles to damaged or aging cells, restoring their energy production and resilience in lab studies, according to a new report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Researchers led by Dr. Akhilesh K. Gaharwar and Ph.D. student John Soukar in Texas A&M University's Department of Biomedical Engineering have developed microscopic, flower-shaped particles known as nanoflowers, made from molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂). In the presence of these particles, stem cells produced about twice the normal amount of mitochondria, effectively turning them into what the team describes as mitochondrial "bio factories." (sciencedaily.com)
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in 2025 (volume 122, issue 43; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2505237122), showed that nanoflower-treated stem cells transferred two to four times more mitochondria to neighboring weakened cells than untreated stem cells. This boosted transfer revived energy production and function in the recipient cells and made them more resistant to cell death, even after exposure to damaging agents such as chemotherapy drugs. (sciencedaily.com)
"We have trained healthy cells to share their spare batteries with weaker ones," Gaharwar, a professor of biomedical engineering, said in a Texas A&M news release. "By increasing the number of mitochondria inside donor cells, we can help aging or damaged cells regain their vitality — without any genetic modification or drugs." (sciencedaily.com)
While cells are naturally capable of exchanging some mitochondria, the nanoflower-boosted stem cells transferred their surplus mitochondria to nearby damaged or aging cells several-fold more efficiently than control cells. "The several-fold increase in efficiency was more than we could have hoped for," said Soukar, the paper's lead author. "It's like giving an old electronic a new battery pack. Instead of tossing them out, we are plugging fully-charged batteries from healthy cells into diseased ones." (sciencedaily.com)
Other approaches to increasing mitochondrial numbers in cells often rely on small-molecule drugs that exit cells quickly and may require frequent dosing. By contrast, the nanoflowers are roughly 100 nanometers in diameter and remain inside cells longer, where they continue to stimulate mitochondrial production. As a result, the Texas A&M team notes that therapies based on this nanoflower technology might only need to be administered about once a month, though this timeline remains a projection based on laboratory findings rather than clinical evidence. (engineering.tamu.edu)
Mitochondrial decline has been linked to aging, heart disease and several neurodegenerative conditions. By strengthening the body's natural capacity for intercellular mitochondrial transfer, the technique could in principle be adapted to many tissues. In interviews with Texas A&M, Soukar suggested that enhanced stem cells might one day be delivered near the heart to address cardiomyopathy or injected into skeletal muscles for conditions such as muscular dystrophy, though such applications remain speculative and will require extensive further testing. (sciencedaily.com)
"This is an early but exciting step toward recharging aging tissues using their own biological machinery," Gaharwar said. "If we can safely boost this natural power-sharing system, it could one day help slow or even reverse some effects of cellular aging." (sciencedaily.com)
The nanoflowers are composed of molybdenum disulfide, an inorganic compound that can form two-dimensional, flower-like structures at very small scales. Gaharwar's lab is among a small number of research groups exploring molybdenum disulfide for biomedical applications, including efforts reported separately in Nature Communications to boost mitochondrial regeneration in other disease contexts. (engineering.tamu.edu)
The work received financial support from the National Institutes of Health, the Welch Foundation, the U.S. Department of Defense, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, the President's Excellence Fund at Texas A&M University and the Texas A&M Health Science Center Seedling Grant program. Key collaborators included Texas A&M researchers Dr. Irtisha Singh, Dr. Vishal M. Gohil and Dr. Feng Zhao. (sciencedaily.com)
While still at an early, preclinical stage, the approach builds on the body's natural mitochondrial exchange system and could open the door to future treatments aimed at slowing or mitigating cellular aging and degenerative diseases, pending further safety and efficacy studies in animals and eventually humans. (sciencedaily.com)